White spots on green bean leaves only mean one thing: Your crop needs your help – and fast.
There are many reasons why these white spots appear, and it is best to understand these causes.
Since there are different ways to address this issue, you need to know what exactly is the culprit.
This is why in our post for today, I’ll share with you common concerns with green bean leaves including the dreaded white spots. Let’s go through each trigger and effective ways to control this unwelcomed phenomenon.

Why There Are White Spots on Green Bean Leaves
In a perfect world, your green bean leaves would be looking perfectly green and lush.
These plants are actually easy and simple to grow. You should be able to grow this legume into any garden, as long as the right conditions are in place.
Green beans come in different varieties such as the bushing and climbing form. No matter what type, though, they are able to produce pods that are tender and edible. These pods may vary in color such as yellow, purple, and the most common green.
Overall, green beans are low-maintenance crops. These are suitable plants to grow for beginners as these are easy to care for.
However, they are not immune to issues. These include fungal diseases, which may cause the green leaves to turn into a white color.
3 Causes of White Spots on Green Bean Leaves
There are a few reasons behind the white spots on green bean leaves. It is essential to understand that cause to determine the right action for you to take.
1. Mildew
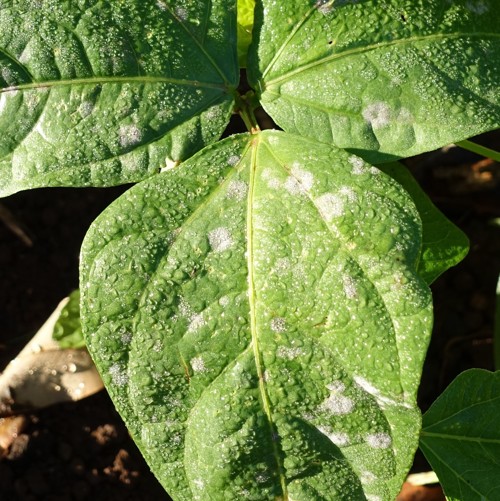

This is the most common reason behind those white spots on green bean leaves. The powdery mildew spreads on the leaves of your green beans, specifically to your older crops.
It usually starts as just a small round spot on an older green bean leaf. When left unaddressed, this issue affects the entire leaf and the other leaves around it. It is a serious problem that concerns parts of the plant that grow above the ground.
The latter stage of the mildew infestation is further damage to the plant. Eventually, the white spots turn yellow. Infected pods will also turn purple over time.
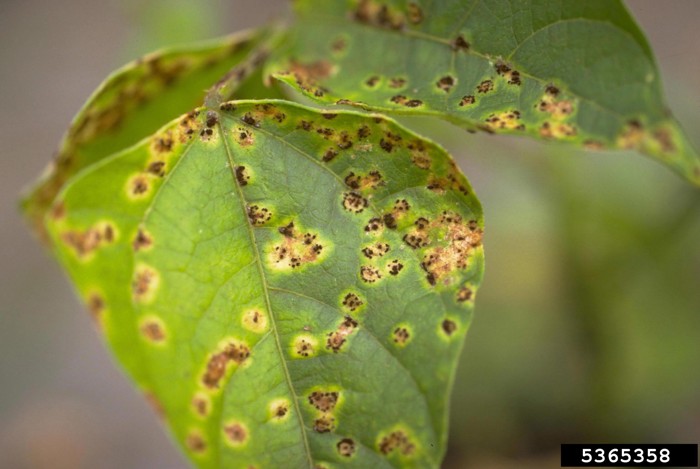
2. Bean Rust
Another concern with green bean plants is bean rust. It also affects older leaves just as the case with mildew.
It begins as a small raised spot on the leaf’s underside portion. The white spots have the typical yellow ring that looks a bit like rust. After about a week, the spots become larger and wider, tuning into a brownish hue.
The upper leaves will start to get these spots and turn yellow. Then, the leaves will dry up and collapse. The affected plant will also start to shed these dead leaves and the issue can even spread to the pods. Thus, the entire crop will die when this problem is not addressed sooner.
The best way to determine if it is bean rust is by touching the infected leaf. Your fingers should end up having this rust-like color, which confirms this issue.
3. Pythium Blight
White spots on green bean leaves can also be due to pythium blight. It is also a type of fungus typical during the summer and when the humidity level is high.
The fungus penetrates into the green bean seeds even before they grow while some crops are affected during the growth period. You will notice the fungus appear like mold and usually found around the soil line.
As the issue progresses, it can also infect the stem, the leaves, and the entire plant.
You can learn more about white spots on your green bean plants by watching this video:
How to Control White Spots on Green Bean Leaves
The best way to control this issue with white spots on green bean leaves is by determining the cause.
For instance, if the issue is due to powdery mildew, the best way to address this concern is by using fungicides with sulfur content. You can also make sure that your soil is well-fertilized with the right nutrients.
Another thing you can do to control powdery mildew is by ensuring ample spacing for your crops. Avoid planting them too close together as this prohibits air circulation.
Additionally, you may thin out the leaves or even get rid of infected plants to save the rest of your crops. Neem oil can also help, as well as the use of Bacillus subtilis, which is a type of fungicide designed for this issue.
In the case of bean rust, you can use a fungicide to address this issue at its onset. If your crops experienced bean rust, you should avoid replanting the same type of crop in the infected location for a minimum of two seasons. Other viable solutions for bean rust include sanitation, weed control, and crop rotation.
Lastly, Pythium blight does not give you many options to reverse the problem once it has started. The only thing left to do is to avoid planting during humid weather for future crops. Treating your green bean seeds before you plant them is also a preventative measure you can take.
Conclusion
White spots on green bean leaves are bad news to many gardeners. However, you can always address the issue while it is not in the advanced stage, yet. By following the tips presented here and as you learn more about the use of the problem, you can determine the most effective solution your crops need. I hope this has been helpful to ensuring the proper growth and development of your crops. Thus, you can expect to harvest healthy green beans and an excellent return on your investment.
Its now showing up on other plants…I am doing Patio gardening. It’s early in the season, may be just throw every thing away and start over. I think all the composting in the soil may have something to do with this. Gardening soils purchased are often over-composted.